Once upon a time, from July to September every year in Southeast Asia region, It was often considered as the most active typhoons period. Many office workers look forward to taking a typhoon vacation when a typhoon comes. Typhoons can often bring abundant water and eliminate the summer heat.
On the premise that no disaster situation like before is reported, typhoons are an important helper for replenishing water resources for reservoirs every year.
However, up to now, not only has no typhoon hit Taiwan, and a few only in Southeast region in the whole of 2022, but this year has set a record for the latest in history where no typhoon warning has been issued. However, The Nanxiu typhoon on August 30, 2022 broke this record.
According to statistics from the Central Meteorological Administration, from 1958 to 2021, the year with the largest number of typhoons in the entire Northwest Pacific was 1964, with a total of 37 typhoons.
It is 11.6 more than the climatic average of 25.4 (average from 1991 to 2020); the lowest year was 2010, when only 14 typhoons were generated, 11.4 average which is less than the climatic average.
In 2022, as of the end of August, only 11 typhoons have been generated in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. If the current situation continues, it is very likely to set a record for the fewest typhoons generated in a single year.
A climate journalist Lamcel M. Plaza reported that: ” The climate in the Philippines is changing in recent years. There are fewer typhoons in last year and the weather is in an unusual manner drier.”
Less and Less Typhoons hit Taiwan
In 1964, there were no typhoons invading Taiwan, which was the least year, but interestingly, it was the year with the largest number of the above-mentioned typhoons.
That is to say, there are 37 typhoons in the Northwest Pacific Ocean, but none of them invade Taiwan.
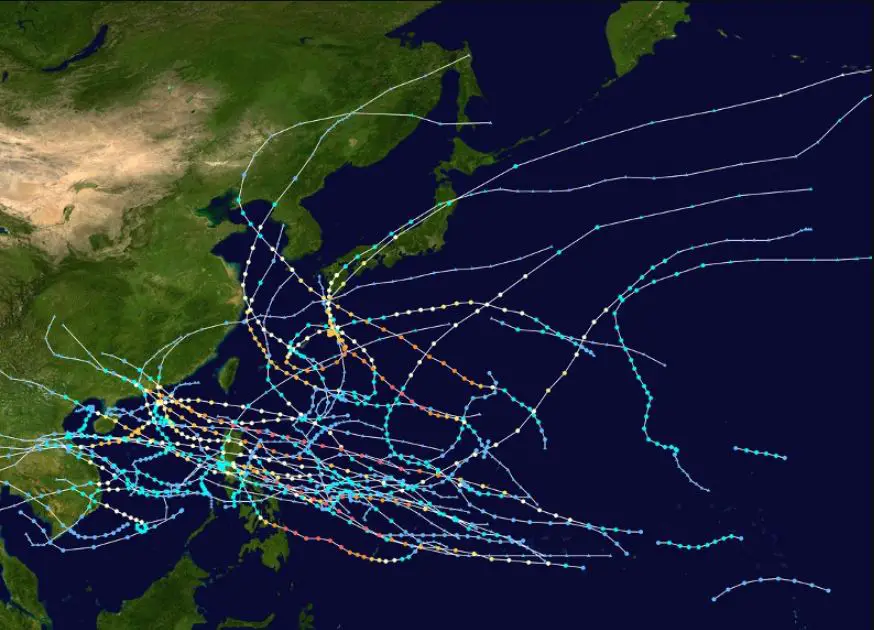
A typhoon is a type of tropical cyclone. Scientifically, it refers to a strong wind with a sustained wind speed of level 12 at the center of a tropical cyclone;
The formation of typhoons all occur on the tropical sea surface. When the temperature is high and a large amount of seawater is evaporated into the air, a low pressure center is formed in the atmosphere.
Under the influence of pressure changes and the earth’s rotation, a typhoon in the northern hemisphere will become a counterclockwise cyclone. As long as there is sufficient moisture and sufficient temperature, it will evolve into a typhoon.
But why are there fewer and fewer typhoons?
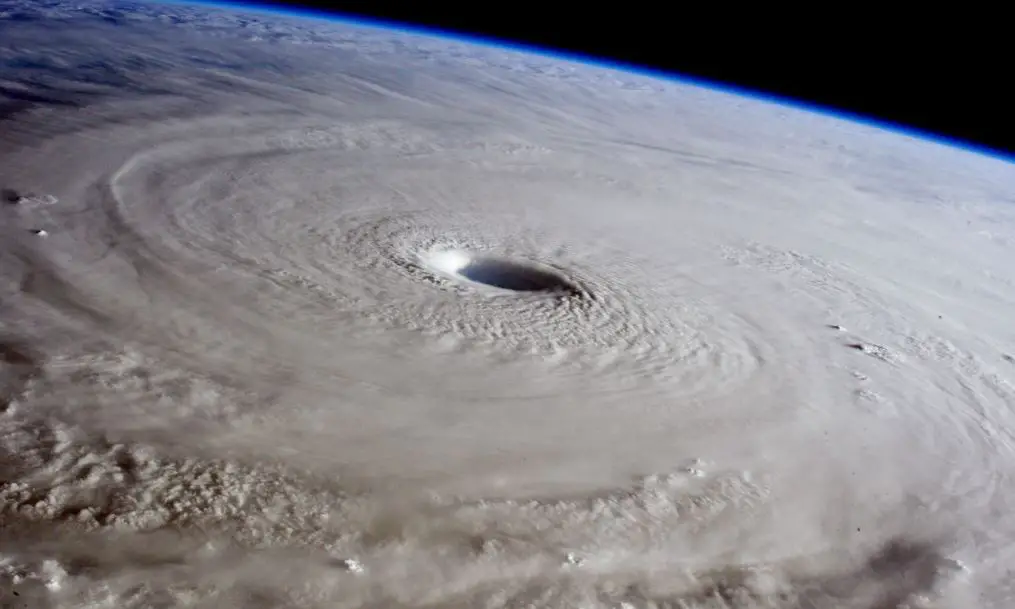

Before the days of artificial satellites, it was almost impossible to know whether a typhoon formed at sea unless a ship unfortunately faced it directly.
For nearly a decade, scientists have been trying to piece together the historical record to ensure a clearer understanding of the climate crisis and how to deal with these storms.
However, the “Nature” study found that the frequency of the most destructive typhoons on Earth has dropped significantly over the past century, scientists say, “With global warming since the 20th century, the annual typhoon, hurricane and tropical The number of storms or tropical cyclones has dropped by 13 percent over the last century,” scientists have found in most of the world’s oceans.
The study found that the formation of a tropical cyclone requires a series of almost identical conditions to allow the thunderstorm extreme cloud system to develop into a typhoon.
Scientists are increasingly convinced that human-caused climate change is causing these conditions to become rarer, but often particularly powerful when they hit the mark.
Although this study found that the frequency of typhoons is decreasing, it does not mean that the threat of typhoons is starting to decrease.
In fact, although the generation of typhoons may become less and less in the future, the threat is bound to become stronger.
Global warming has become the main key factor in the reduction of typhoons
Scientists said that the impact of global warming is that many potential conditions are not conducive to the formation of typhoons, “but even if there are fewer typhoons,
Those typhoons that do form are drawing more energy from the warming atmosphere and ocean, which is the key to why they are getting stronger. “
As the planet warms rapidly and average temperatures continue to rise, extreme weather will become more catastrophic and less predictable.
“The Earth’s climate is changing, and humans are the main cause and initiator of this change, so it’s important to understand the extremes in the context of climate change,” the experts are considered.
The main reason why warming is not conducive to the formation of typhoons lies in the reduction of atmospheric circulation disturbance, and the weakening of circulation reduces the chain reaction, which is naturally not conducive to the formation of typhoons.
Regarding the impact of the El Niño phenomenon, the Central Meteorological Administration stated that the El Niño and the anti-El Niño phenomenon have little impact on the total number of typhoons generated in the Northwest Pacific and the total number of typhoons invading typhoons, but mainly on the location of typhoons.
The Pacific high pressure is weak, the typhoon is moving northward
“Voanews” also revealed that in the past three years, the number of typhoons in Taiwan and the Philippines has not reached the historical average level,
The main reason for this is the increase in water temperature in the central Pacific Ocean, which is mainly where tropical depressions form;
In addition, due to the weak influence of the northern Pacific high pressure, typhoons mainly move northward, which is very different from the traditional typhoons that tend to travel westward.
Many scientists have blamed rising ocean temperatures in the Pacific and Atlantic on a combination of natural conditions and man-made climate change, including the burning of coal, oil and natural gas.
In past studies, it is known that the ocean temperature that is generally formed by typhoons is at least 26 degrees, but at present, there is no study that can confirm how high the temperature is, which will make the formation of typhoons reach a critical value.
Because it must rely on a large number of observations and long-term data to set the tone.
The only thing that can be confirmed is that the problem of global warming has indeed accumulated more conditions that are not conducive to the development of typhoons, and the typhoons that can be formed will be particularly strong.