Computer-aided design, or CAD, brings together computer tools (software and hardware) that make it possible to carry out a geometric modeling of an object in order to be able to simulate tests for manufacturing.
Table of Contents
Principle and use of CAD
CAD provides comprehensive visibility into the behavior of an object before it exists, both in terms of its appearance and its structure and operation. Objects can be represented in two or three dimensions (2D or 3D). Their appearance can be wireframe, solid, surface, it can also simulate texture.
CAD was first widely used, in the United States in particular, by military programs before spreading to other civilian industries: automotive, IT, architecture, civil engineering, aeronautics… IT (hardware and software) and the democratization of tools that have contributed to making CAD a now widespread technology.
Software on CAD
A large number of CAD software are available in open-source:
- Art of Illusion,
- Blender,
- FreeCAD,
- ImplicitCAD,
- QCAD,
- pythonOCC,
- OpenCASCADE
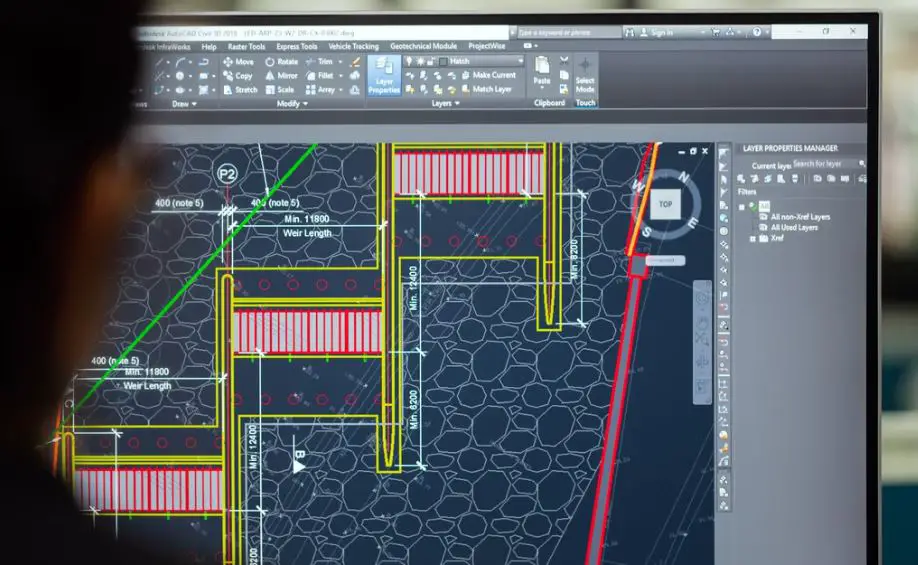
CAD, widely used in mechanics and electronics
CAD is widely used in the mechanical industries by design offices to model and evaluate the behavior of materials, the assembly capacity and the manufacture of parts.
It is also used for the design of electronic circuits and processors. The software makes it possible to assign the behavior corresponding to each component in such a way that it is then possible to simulate its operation.
CAD is very useful for optimizing the layout of components on a printed circuit whose often complex diagrams are spread over several layers. In construction, CAD is used to produce electrical wiring plans from the architect’s plans.
What is CAD?
Computer-aided design (CAD) allows objects to be represented in two or three dimensions on a screen. It includes multiple functions such as numerical calculation, modeling, etc.
A digital design method for manufactured products
The CAD, which is translated into English by Computer-aided design (CAD) includes all the computer tools and simulation methods that allow the design and virtual evaluation of manufactured products, even before they are exist.
It can include CAD, or computer-aided design, but cannot be reduced to it. It allows the computer scientist to represent objects in two or three dimensions and to give them a surface, wireframe, volume, etc. aspects.
Specs of CAD Software
CAD software should be able to do the following:
- Manipulation of 2 or 3D objects,
- Numerical calculation,
- Graphic representation,
- Digital modeling,
- Blueprint drawing,
- The management of large assemblies.
You will find on the Internet a lot of CAD software in free access and specially adapted to your level, whether you are a beginner, intermediate or advanced.
How does CAD work?
A summary of the product to be manufactured
The CAD software makes it possible to establish an exhaustive synthesis of a project by integrating aspects as different as its dimensions, its degree of resistance, its design, etc. It avoids the dispersion of data and combines the various know-how of production processes, including regulatory skills.
The convergence of several professions
The draftsman designs the virtual model of the project from the plans and information that he receives from the engineers and technicians. He must of course know the properties of the materials that will make up the final product and know how to use the most efficient IT tools.
It’s a demanding profession that evolves very quickly and integrates the constraints of sustainable development or the aesthetic choices of customers. The draftsman relies in particular on the project managers who ensure quality, respect for deadlines and budgetary constraints. He works under the supervision of the director of the research department.
What is the CAD used for?
It would be tedious to enumerate the exhaustive list of sectors which call upon the computer-aided design which has become ubiquitous. We could cite as examples the construction, aeronautics, plastics, mechanics, automotive industries, etc. We can thus mention:
- In architect, CAD allows the draftsman to refine buildings by including the architect’s plans, the design, the electrical and electronic installations, the environmental standards of the project and in particular the notion of passive housing.
- In the field of electronics and public works, the technician must be able to simulate digital and analog electronic circuits, to build a printed circuit, to develop the dimensions of an energy distribution installation, etc.
- In mechanics, CAD makes it possible to virtually bend metals and to make retouches to them. It can even simulate the behavior of parts or a machine project. It naturally lends itself to automotive and aviation applications.
- Molecular or orthopedic Medicine, CAD contributes greatly to the progress of medicine which was considerable in the 20th century.