One kilogram of hydrogen energy can be converted into about 39.4kWh of energy. Through today’s commercial electrolyzers, the energy generated is about 52.5kWh.
If you want to popularize hydrogen production from renewable energy, it is necessary to improve the cost-effectiveness of green hydrogen. Now an Australian company has used the new electrolysis technology to achieve an electrolyzer with a conversion efficiency of 95% and 41.5kWh/kg, and has promised to reduce the price of green hydrogen to US$1.50 per kilogram within a few years.
For industries such as steel, heavy-duty transportation systems, chemicals, and more, green hydrogen is a great way to reduce emissions.
According to the forecast of the UK Energy Transitions Commission, due to the above-mentioned industries, it is estimated that the global green hydrogen demand will grow to 500-800 million tons per year by 2050, thereby creating a new industry with a value of several trillion US dollars.
But so far, green hydrogen technology is still stuck in the conversion efficiency and price threshold.
Renewable energy hydrogen production cannot be compared with traditional fossil fuel hydrogen production in terms of efficiency and price. Ultra-efficient electrolysis launched by Australian company Hysata may improve the cost competitiveness of green hydrogen, accelerate the speed of global decarbonization, and improve the energy security of various industries.
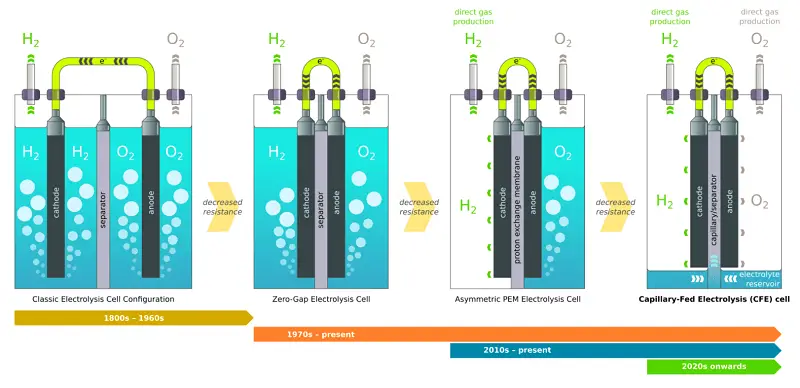
Hysata’s electrolyzer: How it works
Different from the traditional electrolysis cell where the electrodes are completely immersed in the electrolyte, the electrolyte of Hysata’s capillary-fed electrolysis cell is stored in the bottom storage tank, so the anode and cathode electrodes do not come into direct contact with the liquid, which naturally does not allow bubbles. The bubbles hinder the hydrogen production effect of water splitting.
Hysata’s electrolyzer mainly uses a porous, hydrophilic separator between the cathode and anode, and uses capillary action to suck up the electrolyte. Only one side of the electrode will contact the electrolyte, which can directly generate hydrogen and oxygen without any air bubbles.
The Hysata team claims that the efficiency of the capillary action electrolyzer is as high as 98%, which has also been confirmed by the industry in Nature Communications, and the efficiency is also better than that of the current commercial electrolyzer for electrolysis of water for hydrogen production, with an average efficiency of 83%.
This design also eliminates the need for liquid circulation, gas-liquid separation tanks, pipelines and pumps, and works with either air or radiant cooling, further reducing capital and operating costs .

Reducing the capital and operating costs of green hydrogen
Gerry Swiegers, Chief Technology Officer of Hysata, pointed out that Hysata capillary electrolyzers are designed to simplify manufacturing, be easy to expand and install, and provide an overall system efficiency of 95%, equivalent to 41.5 kWh/kg, compared to 75% or less efficiency of existing electrolyzer technology , which can effectively reduce the capital and operating costs of green hydrogen.
Paul Barrett, CEO of Hysata, said that the technology is gradually being commercialized in the future.
He expects to reach GW-scale hydrogen production capacity in 2025, when it has the opportunity to reach $1.50 per kilogram of hydrogen, and is now planning to build a pilot electrolyzer manufacturing plant.The company also hires dozens of employees this year (2022).
Image Credit: Hysata