Some parts of the world are currently experiencing an alarming period of drought. In some areas, the amount of precipitation has fallen far below normal. And the announcement made by the researchers confirms this. A new planetary boundary for the freshwater cycle has been crossed.
The report was first published in 1970
In the early 1970s, a report published for the first time by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT, USA) evaluated the impact of human activity on our Earth for the first time. The Meadows report warned:
The increasing consumption of our planet’s resources will push us towards a wall. A wall erected on the way to our 21st century. A wall that will prevent us from freely accessing natural resources. The result is a dramatic deterioration in our living conditions. This could even lead to the death of our civilization.

The condition of our planet has gotten much worse in the past 50 years
More than just a wall, the Meadows report introduced the concept of planetary boundaries 50 years ago. But since then, our resource consumption has continued to increase. So much so that before 2022, four of these planetary boundaries, more or less interconnected and more clearly defined by scientists from 2009, had already been crossed.
Those related to change in land use affecting the integrity of biodiversity, disruption of phosphorus and nitrogen cycles, and climate change. In January this year, researchers from the Stockholm Resilience Center (SRC, Sweden) announced that a fifth limit had been crossed: the one on chemical pollution.
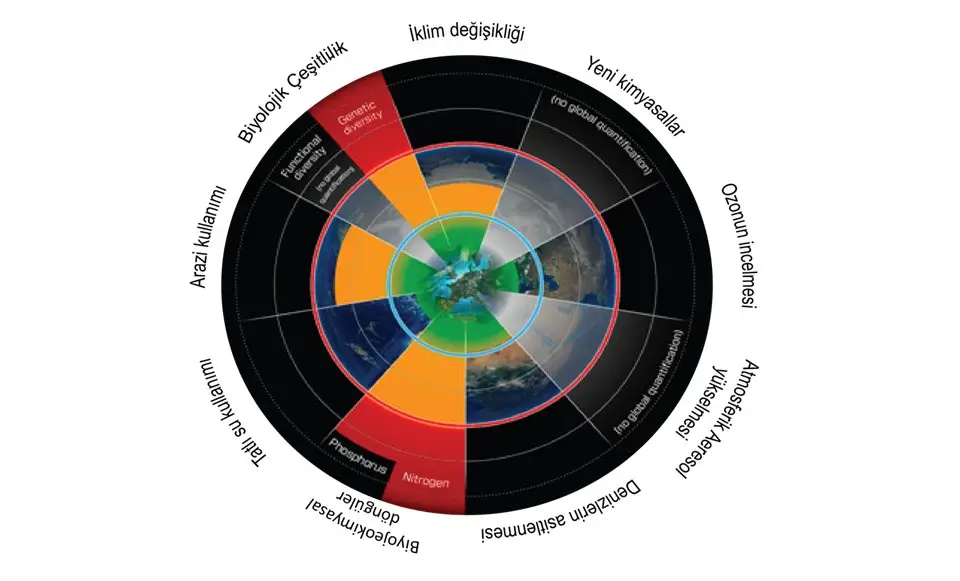
Freshwater cycle limit exceeded
A few days ago the same team came back to give us more bad news. From the nine planetary limit in total, the sixth planetary limit to the Freshwater cycle has also been exceeded. And that will result in an alarming period of drought for most countries.

Water is the blood of the biosphere. But our activities are profoundly changing its cycle. This now impacts the health of the entire Planet,” explains Lan Wang-Erlandsson, lead author of the SRC study, in a press release from Siwi. The work led by the researchers shows that today disruptions to the freshwater cycle are a real risk for ecosystem collapse.
For example, the survival of the Amazon rainforest is highly dependent on soil moisture. In addition to deforestation, a drop in this humidity due to global warming now directly threatens entire areas of this precious green space.
Image source: Unsplash