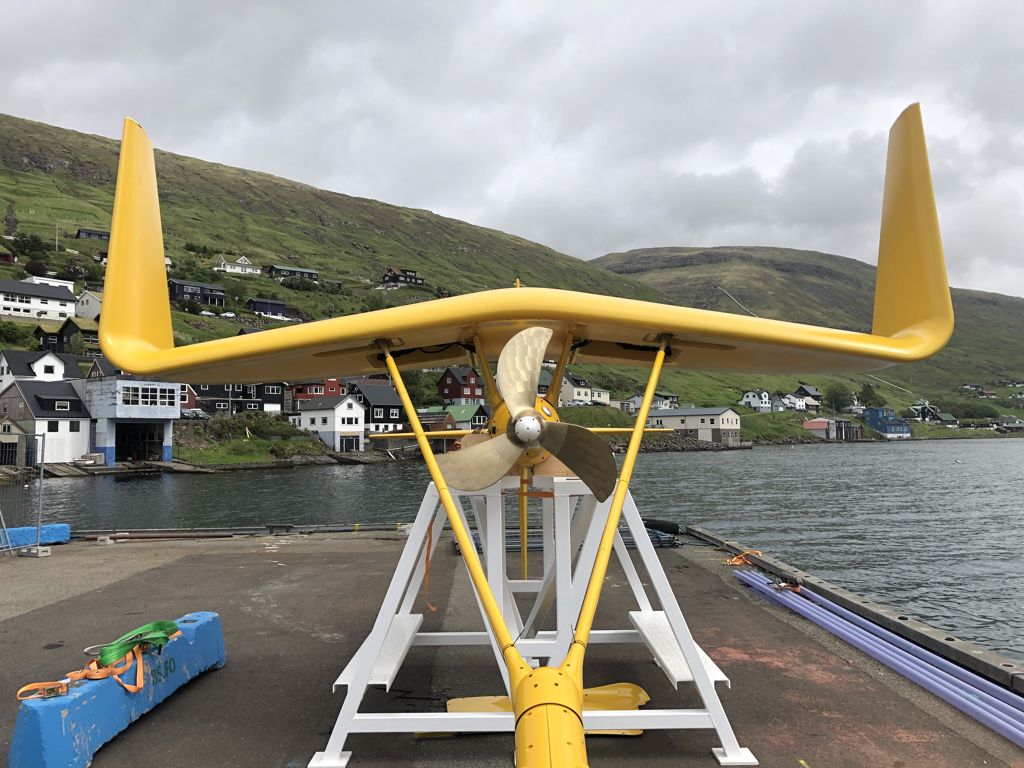
This extraordinary desalination device is powered by mechanical power from waves as it floats in the ocean, producing up to 13,000 gallons (53,000 liters) of fresh water per day. It uses wave energy as its power source and this device is made from 170,000 recycled PET bottles. In addition, the concentration of discharged brine is much lower than other devices that perform the same function.
Projects such as these are of great importance as fresh water resources are limited in the world.
Only 3% of the world’s water is fresh water, and the vast majority of it is glaciers. If we remove the glaciers from the freshwater sources, only 1% is left. Thus, humanity finds itself facing critical freshwater scarcity on the most humid planet in the solar system, affecting nearly half of its population despite being surrounded by water. Countries that face water scarcity are establishing mega sea water treatment plants with huge investments.
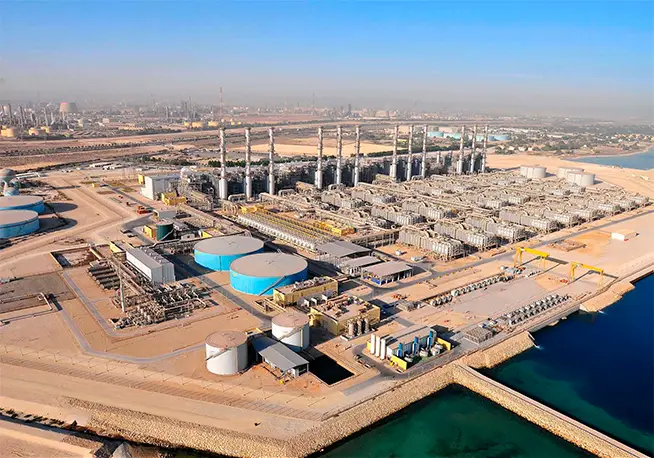

Mega purification plants harm the environment
These mega facilities, which were established to meet the water needs, cause some serious problems. First, it will require huge amounts of energy as it scales up, and this is when the transition from dirty energy to clean energy is difficult, when power is at its peak.
Second, land-based industrial desalination plants take huge volumes of brine, then remove most of the water and pump high concentrations of salty brine back into the ocean, often contaminated with chemicals used to pre-treat the water and hold equipment.
Oneka; showcased its project that offers a holistic solution
These plants, which need a lot of energy, also dump too much salt back into the oceans, posing a great risk to ocean-dwelling creatures.
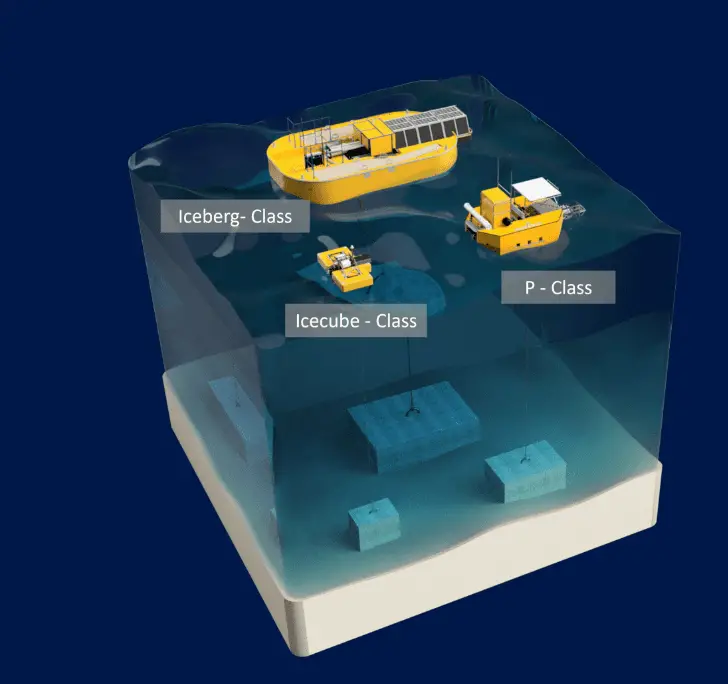
Oneka’s wave-powered floating desalination buoys could be an invaluable development, as they set out to find solutions to problems like these.
They operate entirely on wave power. Anchored to the seafloor anywhere with an average wave height greater than 1 m (~3 ft), they absorb energy from passing waves and convert it into mechanical pumping forces that pull seawater and push a quarter in the opposite direction.
They use the osmosis desalination system to create drinkable water. The clean water produced is pumped to land using high-density polyethylene pipelines.
The resulting wastewater brine is remixed with seawater and discharged into the sea, so the salinity of the resulting water is only 30% higher than the surrounding seawater, which basically does not affect the marine ecology.
Compared to land desalination plants, the scale of floating desalination plants is quite small. Equipment withstands waves to survive, naturally facing highly corrosive waves every day, so it needs to be overhauled 3 to 7 times a year, but the designed service life is as long as 15 to 20 years.