The US Space Agency has announced a collaboration with start-up SpinLaunch to send an object into low orbit.
The objective is to test the capabilities of the centrifuge which could become an economical and ecological alternative to conventional rockets.
NASA directs its research towards new horizons and relies on… a large centrifuge. In a press release issued on April 6 by the Business Wire site , the American space agency announced the start of a collaboration with the young Californian company SpinLaunch.
The objective is to test, from 2022, the capacities of the project carried out by the company: sending satellites and objects into orbit thanks to the kinetic force caused by a centrifuge. Thanks to the signing of a Space Act Agreement , NASA will be able to provide its expertise while analyzing the possibilities offered by this innovative system.
Spinlaunch Centrifuge Rocket Launcher simulation Video
An ecological and economical solution
Founded in 2014 , SpinLaunch promotes an ecological and economic evolution of space exploration. Its system is based on a massive structure called an “ orbital mass accelerator ” ( L100 Orbital Mass Accelerator). This titanic drum 50 meters high and 33 meters in diameter has within it a large arm to which a projectile would be attached. The rotation of the arm, gradually gaining speed, would increase the kinetic energy of the object to be propelled into space.
Once the velocity was high enough, the projectile would be sent vertically from a tube adjacent to the drum, similar to a chimney . The force caused by the rotation of the object would potentially reach between 9,000 and 10,000 G. By comparison, the force exerted on astronauts taking off in a Soyuz capsule is equivalent to 5 G.
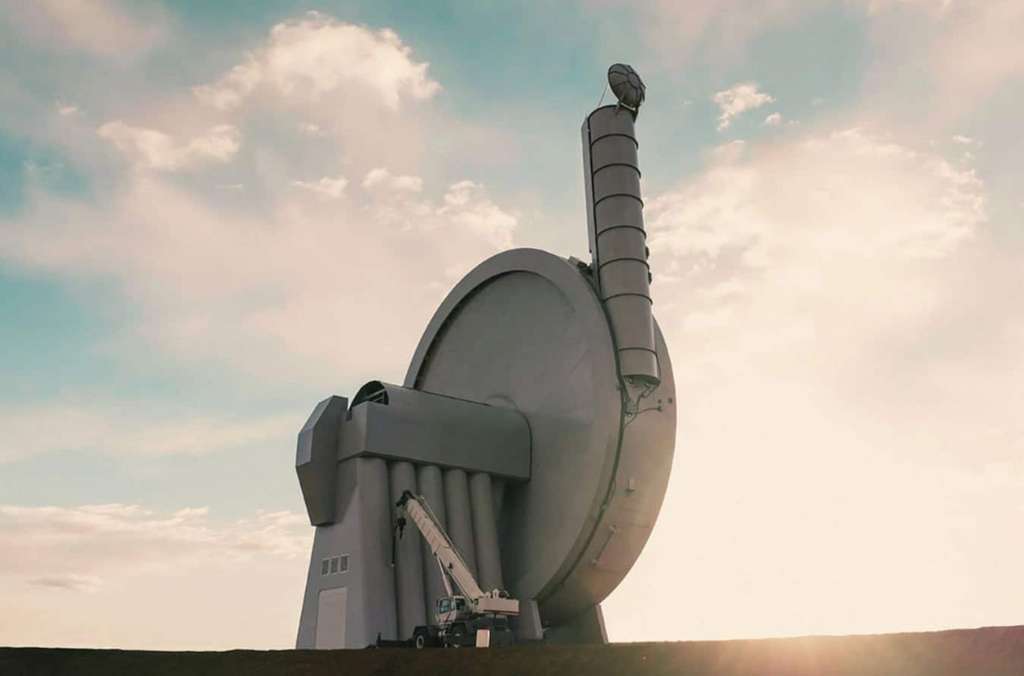

One of the advantages of the system developed by SpinLaunch is its ecological aspect: the launches require approximately 70% less fuel than the take-offs of traditional launchers . The CEO of the company, Jonathan Yanley, thus affirmed that SpinLaunch was a real alternative to polluting rockets in the face of the constant increase in missions to space, with the sending of armadas of satellites such as the Starlink constellations . or OneWeb. These devices would thus require less fuel to adjust their positions once in low orbit.
At the same time, the SpinLaunch centrifuge is also intended to be economical, allowing the launch of satellites into space at a lower cost. Depending on the vehicle used and the load carried, sending a probe into orbit can cost several million euros, or even tens of millions. Thus, an Ariane 5 can carry nearly 20 tons of payload for the modest sum of 170 million euros. SpinLaunch wants to reduce these considerable fees, with a cap of $500,000 per launch.
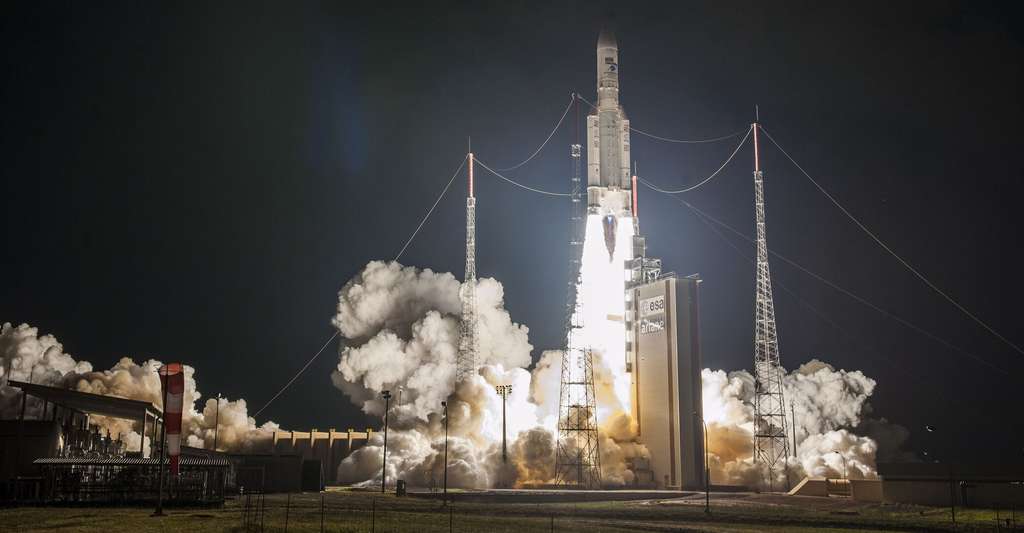 Take-off of an Ariane 5 from the Kourou base, in French Guiana. © ESA
Take-off of an Ariane 5 from the Kourou base, in French Guiana. © ESALaunch imminent for SpinLaunch?
SpinLaunch’s centrifuge is only in its experimental phase, but a first test carried out in October 2021 demonstrated the feasibility of the project. A three-meter-high object had been propelled 10,000 meters above sea level, at a speed of more than 8,000 kilometers per hour.
A first success for the company, the engineers having pointed out that the centrifuge had only operated at 20% of its theoretical maximum power.

The collaboration between NASA and SpinLaunch could accelerate the development of the project.
The firm had previously indicated that, to send 200 kg satellites into space, the diameter of the centrifuge had to increase proportionally to reach a hundred meters. SpinLaunch and the space agency are expected to conduct a first joint test sometime in 2022.